Rollback des Dodd- Frank Acts, Pleite der SVB und Chinas neue Regulierungsbehörde und Zentrale Technologiekommission als Modell eines safe haven
Die Silicon Valley Bank, eine Venturecapitalbank für Startups der sci-tech- und Hitech-branche ist zahlungsunfähig. Wenn man Trump glaubt, steht eine neue Finanzkrise , ein neues 1929 und 2008 an. Biden macht er dafür verantwortlich, weil der die Steuern erhöht habe. Abet hängt der Kollaps der SVB überhaupt mit den Steuererhöhung und wenn mit welchen ursächlich zusammen?
„Trump nach Bankenkollaps im Panikmodus: „Sie beginnen bereits zusammenzubrechen“
Erstellt: 13.03.2023, 17:10 Uhr
Donald Trump hat mit einer Brandrede auf die Insolvenz der Silicon Valley Bank reagiert und eine bevorstehende Wirtschaftskrise prognostiziert.
Washington – Der frühere US-Präsident Donald Trump hat nach die Ängste der US-Amerikaner vor einer erneuten Finanzkrise weiter befeuert. In einem Beitrag auf seiner eigenen Social-Media-Plattform „Truth Social“ veröffentlichte Trump eine regelrechte Brandrede und präsentierte seinen Followern auch gleich einen Schuldigen. Der hieß wie so oft Joe Biden.
Donald Trump attackiert Biden: „Die Banken beginnen bereits zusammenzubrechen“
„Mit dem, was mit unserer Wirtschaft passiert, und mit den Vorschlägen zur größten und dümmsten Steuererhöhung in der Geschichte der USA mal fünf, wird Joe Biden als der Herbert Hoover der modernen Zeit untergehen“, polterte der ehemalige Präsident auf dem Kurznachrichtendienst. „Wir werden eine Große Depression haben, die viel größer und mächtiger als die von 1929 sein wird. Zum Beweis: Die Banken beginnen bereits zusammenzubrechen!“, prognostizierte der 76-Jährige in Großbuchstaben weiter.
Herbert Hoover war der 32. Präsident der Vereinigten Staaten und hielt das Amt während der Weltwirtschaftskrise und der darauffolgenden „Great Depression“ in den USA inne. Trump sieht die Weichen für eine erneute Weltwirtschaftskrise offenbar bereits gestellt.
Trump im Panikmodus: Silicon Valley Bank insolvent – Angst vor Dominoeffekt
Die Lage, auf die sich der frühere Präsident bezieht, ist in der Tat ernst. Am Freitag hatten die US-Behörden die Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) geschlossen. Das Geldinstitut war infolge von Milliardenverlusten beim Verkauf von Wertpapieren in massive Schwierigkeiten geraten. Bei dem Schritt handelte es sich um den größten Bankenkollaps seit dem Höhepunkt der Finanzkrise 2008. Damals hatte die Bank Washington Mutual Insolvenz anmelden müssen. In der Branche herrscht nun Angst vor einem Dominoeffekt, der weitere Geldinstitute mit in die Tiefe reißen könnte.
US-Regierung arbeitet an „Lösung“ – Biden kündigt Konsequenzen an
US-Finanzministerin Janet Yellen hatte eine staatliche Rettung der SVB am Samstag ausgeschlossen. In einem Interview mit dem US-Sender CBS sagte Yellen jedoch, man wolle „sicherstellen, dass die Probleme einer Bank nicht zu einer Ansteckung anderer, gesunder Banken führen“. Die Regierung arbeite nun mit dem Bundeseinlagensicherungsfonds FDIC an einer „Lösung“ für die Kunden der Bank.
Präsident Biden kündigte ebenfalls am Sonntag an, die Verantwortlichen für die Insolvenz zur Rechenschaft zu ziehen. „Die amerikanische Bevölkerung und die amerikanischen Unternehmen können darauf vertrauen, dass ihre Bankeinlagen da sind, wenn sie sie brauchen“, führte Trumps Nachfolger aus. Der Staatschef kündigte an, sich am Montag zum Bankensystem äußern zu wollen.
„Trump hatte mit allem recht“: Ex-Präsident poltert auf eigenem Netzwerk
Für Donald Trump scheinen die USA jedoch bereits auf dem Weg in die nächste Finanzkrise zu sein. „Trump hatte mit allem recht“, schrieb der Ex-Präsidenten nach seiner Brandrede am Sonntag in einem weiteren Post auf Truth Social. Trumps Wähler werden die jüngsten Entwicklungen wahrscheinlich als weiteres Zeichen für die Unfähigkeit von Joe Biden ansehen und sich die Rückkehr von Trump ins Oval Office wünschen. (fd mit AFP)
Ursächlicher ist da Trumps neoliberales handeln, denn Trump hatte ja die nach der Finanzkrise vorgenommene Bankenregulierung des Dodd-Frank Act zurückgerollt und die zu regulierende Bankengröße von 50 Mrd.$ auf 250 Mrd.$ ausgeweitet. 1929 tat Hoover nichts gegen den Black Friday, was ihm Wirtschaftsexperten ja als politischen Fehler bestätigten und die Geburtsstunde des antizyklischen sttaatsinterventionistischen Keynesianismus wurde. Anders als Hoover scheint aber Biden frühzeitig zu handeln und zwar nach Draghis Motto: Whatever it takes, nun ala Biden: Whatever is needed.
“Biden says to do ‚whatever needed‘ as banks hit despite SVB action
US regulators on Sunday stepped in after the collapse of SVB – the largest US bank failure since 2008, which suffered a run after a big hit on a portfolio of bonds.
Updated: March 13, 2023 16:21
US President Joe Biden pledged on Monday to do whatever was needed to address a banking crisis threatened by the collapses of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank which forced regulators to step in with emergency measures.
Biden’s address came after weekend moves by the United States to guarantee deposits at collapsed tech-focused lender SVB failed to reassure investors about the health of other banks around the world.
Europe’s STOXX banking index fell 5.8% on Monday and was on track for its biggest two-day fall since March 2022, soon after Russia invaded Ukraine. Germany’s Commerzbank fell as much as 12.7%, while Credit Suisse hit a new record low after falling more than 15%.
Biden said his administration’s rapid action over the weekend should give Americans confidence that the US banking system is safe, adding that he was going to ask Congress and regulators to strengthen bank rules.
„Americans can have confidence that the banking system is safe. Your deposits will be there when you need them.“
US bank shares had declined in pre-market trading, with Bank of America down 3.7%. Smaller lenders remained under pressure with privately owned First Republic Bank plunging around 60% and PacWest PACW.O down around 40%.
In the money markets, a closely-watched indicator of credit risk in the US banking system edged up, as did other indicators of credit risk in the eurozone. Europe’s volatility index jumped to its highest level since October 2022.
Meanwhile, the price of gold raced towards the key $1,900 level, emboldened by bets that the US Federal Reserve may have to tone down its rate hikes as investors sought safe havens.
„There is a sense of contagion and where we see a repricing around financials is leading to a repricing across markets,“ said Mark Dowding, chief investment officer at BlueBay Asset Management in London.
Dowding said he did not think that a lot of the issues affecting US banks would be present in European lenders.
Bonds held by SVB were „worth next to nothing in a short space of time, so against that backdrop, that has an effect that is translated on a more widespread basis,“ he added.
US regulators on Sunday stepped in after the collapse of SVB – the largest US bank failure since 2008, which suffered a run after a big hit on a portfolio of bonds.
SVB’s customers will have access to all their deposits starting Monday and regulators set up a new facility to give banks access to emergency funds. The Federal Reserve also made it easier for banks to borrow from it in emergencies.
Regulators moved swiftly too to close New York’s Signature Bank SNBY.O, which had come under pressure in recent days. But more stress is expected.
First Republic Bank said on Sunday it had secured additional financing through JP Morgan Chase, giving it access to a total of $70 billion in funds through various sources.
European fallout
In Germany, the central bank convened its crisis team on Monday to assess the possible fallout on the local market, even as no emergency action was foreseen in Europe.
Swiss financial regulator FINMA said it was closely monitoring the situation surrounding failed US lenders and looking for signs of contagion from the banks‘ collapse.
After marathon talks over the weekend, early on Monday in London HSBC HSBA.L announced it was buying the British arm of SVB for one pound ($1.21). It said Silicon Valley Bank UK had loans of around 5.5 billion pounds and deposits of around 6.7 billion pounds as of March 10.
While SVB UK is small – HSBC’s balance sheet exceeds $2.9 trillion – concerns that SVB’s failure would cause Britain’s start-up industry to seize up had prompted calls from the sector for government to intervene.
Markets gyrate
Meanwhile, a furious race to re-price interest rate expectations also sent waves through markets as investors bet the Fed will be reluctant to hike next week while the mood is febrile and delicate.
Markets are now pricing in a roughly 40% chance that the US central bank will not raise rates at all, according to the CME’s Fedwatch tool. Earlier last week a 25 basis point hike was fully priced in, with a 70% chance seen of 50 basis points.
Two-year US Treasury yields were last down 55 bps at around 4.09% US2YT=RR set for their biggest one-day fall since 1987 according to Refinitiv data. SVB’s collapse comes alongside the closure of crypto-focused bank Silvergate, which last week disclosed plans to wind down operations and voluntarily liquidate, in the aftermath of FTX’s implosion last year.
US banks lost more than $100 billion in stock market value late last week following SVB’s failure, European banks have now lost a similar amount, a Reuters calculation showed.
https://www.jpost.com/breaking-news/article-734178while
Zwar wird die SVB nicht verstaatlicht, aber die Einlagen gesichert.Zudem schiebt Biden die Schuld zurück auf Trump wegen des Rollbacks des Dodd- Frank Acts, wobei die Frage ist, warum er diesen selbst nicht wieder in kraft setzte, als er an die Regierung kam.
„US- Präsident Biden beruhigt US-Kunden nach Bankpleiten
Der Crash zweier US-Banken weckt dunkle Erinnerungen an die Finanz- und Bankenkrise von 2008. Washington reagiert schnell, um eine Panik bei den Anlegern zu verhindern. Wer ist an der Misere schuld?
Aktualisiert: 13.03.2023, 17:53
Washington. US-Präsident Joe Biden hat nach der Schließung zweier Banken Kunden beschwichtigt. „Die Amerikaner können beruhigt sein, das Bankensystem ist sicher. Ihre Einlagen sind sicher“, sagte Biden. Kunden der betroffenen Institute hätten ab Montag Zugriff auf ihre Ersparnisse. Das gelte auch für kleine Betriebe. Die Kosten für die Einlagensicherung sollen nicht die Steuerzahler tragen. Das Geld komme aus einem Einlagensicherungsfonds, in den alle Banken einzahlten, sagte Biden.
Der Schutz gelte allerdings nicht für Investoren. Diese müssten ihr Risiko selbst tragen. „So funktioniert der Kapitalismus“, sagte Biden. Außerdem würden die Manager der unter staatliche Kontrolle gestellten Banken gefeuert. „Wenn die Bank von der Einlagensicherungsbehörde übernommen wurde, sollten die Leute, die die Bank geführt haben, dort nicht mehr arbeiten“, betonte der Präsident.
Unruhe an den Märkten
Am Freitag war die auf Start-up-Finanzierung spezialisierte Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) nach einer gescheiterten Notkapitalerhöhung vorübergehend geschlossen und unter staatliche Kontrolle gestellt worden. Das sorgte weltweit für Unruhe. Auch andere Banken gerieten an der Börse unter Druck. Am Sonntag wurde auch die in New York ansässige Signature Bank geschlossen.
Auch die deutsche Zweigstelle der SVB mit Sitz in Frankfurt wurde am Montag dichtgemacht. Sie sei mit sofortiger Wirkung für den Kundenverkehr zu schließen, verfügte die Finanzaufsicht Bafin. Wegen „der bestehenden Gefahr für die Erfüllung der Verpflichtungen gegenüber Gläubigern“ erließ die Bafin ein Veräußerungs- und Zahlungsverbot gegenüber der Bank. „Die Notlage der Silicon Valley Bank Germany Branch stellt keine Bedrohung für die Finanzstabilität dar.“
An den Finanzmärkten blieb die Lage angespannt. Auch wenn die Einlagengarantie der Regierung zum Börsenstart an der Wall Street am Montag zunächst etwas Wirkung zu zeigen schien, blieb die Nervosität bei Bankaktien hoch. So wurden die Titel einiger US-Regionalbanken nach heftigen Kursverlusten zeitweise aus dem Handel genommen. Auch die Papiere größerer Geldhäuser wie Bank of America, Wells Fargo und Citigroup gerieten unter Druck.
„Wissen, wer verantwortlich ist“
Indes läuft in den USA die Suche nach Schuldigen nach dem SVB-Kollaps auf Hochtouren. So sind die unter dem damaligen US-Präsidenten Donald Trump beschlossenen Lockerungen der im Zuge der Finanzkrise 2008 verschärften Bankenregeln in den Fokus geraten. „Wir wissen, wer verantwortlich ist“, hieß es in einem in der „New York Times“ veröffentlichten Beitrag der demokratischen Senatorin und bekannten Wall-Street-Kritikerin Elizabeth Warren. Die derzeitige Bankenkrise sei eine direkte Folge von Finanzregeln, die in der Trump-Ära von der Politik und der Notenbank Fed aufgeweicht worden seien.
Auch Biden machte Trump verantwortlich. Präsident Barack Obama, dessen Stellvertreter Biden war, habe scharfe Auflagen erlassen, damit sich die Finanz- und Bankenkrise nicht wiederhole. Unter Trump seien einige dieser Auflagen zurückgefahren worden.
2018 hatte der US-Kongress den Weg für eine Rücknahme wesentlicher Teile des sogenannten Dodd-Frank-Gesetzes freigemacht, das erneute Bankenpleiten zulasten der Steuerzahler verhindern sollte. Trump hatte der Finanzlobby bei seinem Amtsantritt 2017 versprochen, die 2010 verabschiedeten Regeln zurückzudrehen. Trump bezeichnete das Dodd-Frank-Gesetz als „Desaster“, das er am liebsten ganz abschaffen würde. Das geschah zwar nicht, doch für kleine und regionale Banken – die jetzt Probleme haben – wurden die Auflagen erleichtert.
interessant, wie China die Pleite von SVB sieht. Als Ausdruck ,dass die durch die zunehmende US-Verschuldung und Hochzinspolitik langeschlummernden Risiken nun zu periodischen Instabilitäten führen, wobei in den USA noch an die 190 Banken risikoanfällig seien .Stärkere Regulierung wird gefordert und Chinas neue Finanzregulierungsbehörde als Model gesehen, wie man mit diesen Risiken umgeht .Zudem seien anders als die westlichen Banken die Aktienwerte chinesischer Banken gestiegen, China eine Art Safe Haven, weswegen wahrscheinlich die ausländischen Investitionen in Chinas A-Markte fließen würden.
„SVB collapse highlights need to strictly maintain the bottom line of low risks: former Chinese finance minister
By Song Lin Published: Mar 18, 2023 05:08 PM Updated: Mar 18, 2023 05:09 PM
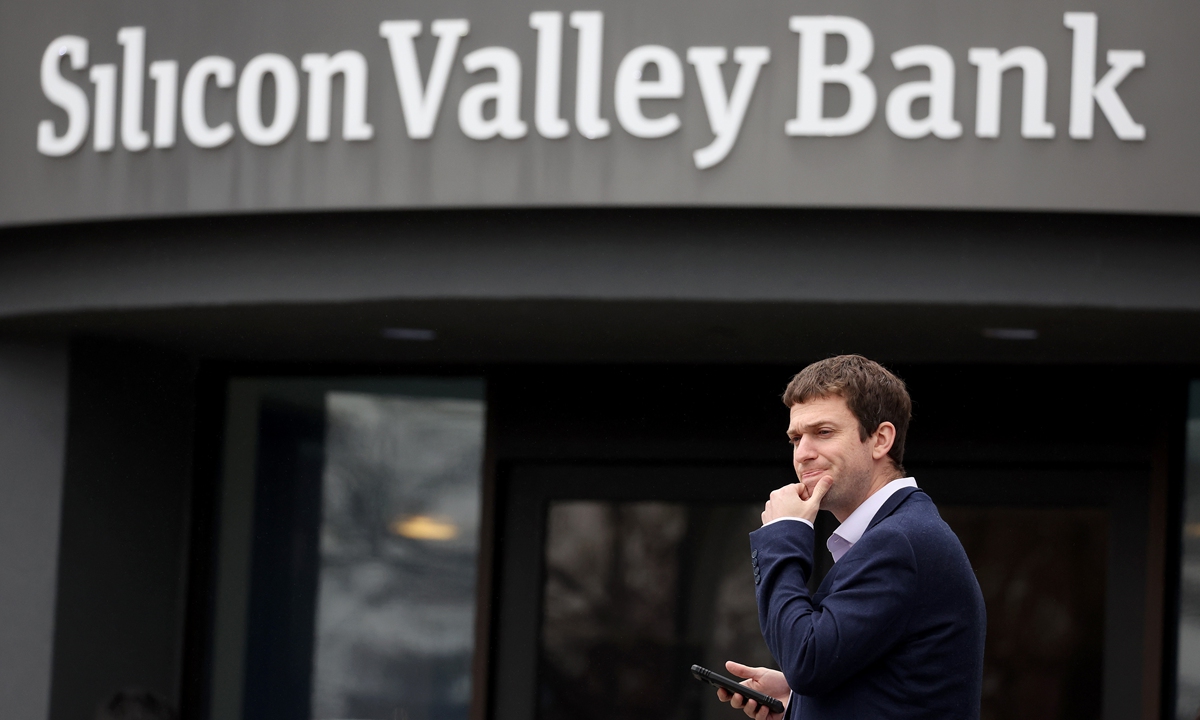

A customer stands outside of a shuttered Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) headquarters on March 10, 2023 in Santa Clara, California
It is crucial to improve the financial regulatory system and strictly maintain the bottom line of low risks, China’s former finance minister said at a forum on Saturday in commenting on the recent collapse of the US Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) that sent shockwaves across the US banking system.
The SVB bankruptcy suggests that financial markets have been hit by monetary policy changes, Lou Jiwei, director general of the Global Asset Management Forum and China’s former finance minister, said at the ongoing annual session of the forum, according to media reports.
The unconventional monetary and fiscal policies adopted by some countries during the COVID-19 pandemic have led to high leverage ratios across governments, households, enterprises, and financial institutions. These ratios rose quickly but would not fall easily, Lou said.
It has exacerbated the hikes of the inflation and its impact has been extended to the global financial market, with soaring volatility in stocks, bonds, foreign exchange markets, Lou said, noting that from a historical perspective, it may lead to a new round of crisis spilling over into emerging markets.
As the US 16th largest lender, SVB faced meltdown on March 10 after a 48-hour run on deposits. It marked the largest bank crash since the 2008 financial crisis. When many were still pondering whether it was another Lehman Moment that started the global financial crisis over a decade ago, the US 29th biggest lender Signature Bank closed by regulator just two days after the SVB collapse.
The unexpected bank failure has soon sent shockwaves across the US banking system, with jitters spreading across the global market.
NASDAQ Bank index, which contains securities of NASDAQ-listed banks, dropped 22 percent from 3981.59 on March 8 to 3100.16 on March 17. The First Republic Bank saw its share price plummeted from $115 to $23.03 during the period, down nearly 80 percent.
In Europe, alarms sounded at Credit Suisse, a 167-year-old Swiss bank which is also the 17th largest lender across Europe. Its share price has lost 30 percent since March 8. Although the bank secured a $54 billion loan from Swiss central bank to shore up its liquidity, its investor sentiment remains fragile.
The bank failure and emergency showed that the long-simmering profound financial risks in Europe and the US have reached a critical point of periodic outbreak, Dong Shaopeng, a senior research fellow at the Chongyang Institute for Financial Studies at Renmin University of China, told the Global Times on Saturday.
Banks are professional risk managers, and if they cannot manage risk effectively, then it means that the risk control system has failed, Dong said.
SVB is not the only risk point, a total of 186 US banks have reportedly been exposed to similar risks. “Even if only half of uninsured depositors decide to withdraw, almost 190 banks are at a potential risk of impairment to insured depositors, with potentially $300 billions of insured deposits at risk,” read an analysis conducted by New York-based Social Science Research Network.
Counting on its advantages as the world’s dominant financial power, US policymakers have believed that they could reap interests of others to plug their own loopholes. It is such “financial confidence” which has supported them to adopt a radical quantitative easing and then a drastic tapering policy, Dong said.
Yet, a considerable number of emerging countries are attaching more importance to financial risk management and firmly safeguarding their own autonomy, Dong said.
China has attached great importance to preventing and defusing systemic risks, and it is further improving its financial regulation including setting up a central commission for finance following the two sessions to optimize and adjust setting and functions of regulatory institutions, Lou said.
Lou said that China will continue to cooperate with other countries in financial regulation to jointly forestall and defuse systemic risks in the global financial system and maintain stability and prosperity of the global financial market.
The People’s Bank of China (PBC), the nation’s central bank, recently stressed the overall financial market is running smoothly and risks are under control. Large banks with excellent ratings are the “ballast stone” of China’s financial system. Reforms of a few problematic small and medium-sized financial institutions have achieved important progress, and illegal financial activities have been effectively curtailed, it said.
Amid a steep drop in the value of global banking shares following the SVB meltdown, however, Chinese banking shares rallied collectively. The Bank of China saw its share price surged from 3.33 yuan ($0.48) on March 8 to 3.48 yuan on March 17, reaching a five-year high.
The Chinese economy has contributed more than 30 percent of global growth annually for the past two decades, and this momentum will continue in the future, Yang Delong, chief economist at Shenzhen-based First Seafront Fund Management Co, told the Global Times on Saturday.
Under such circumstances, China’s strong enterprises, robust core assets will remain very attractive to foreign investment, Yang said, predicting that it is highly likely that the inflow to China’s A-share market from overseas investor will exceed 300 billion yuan this year.
https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202303/1287515.shtml
Zudem hält die KP China die Auswirkung der SVBpleite und westlicher Banken auf China für relativ begrenzt, zudem die chinesische Finanzmärkte und Hitechunternehmen samt Start ups gut reguliert seien und auch keine Schlupflöcher wie das neoliberale US-Finanzsystem vorweisen würden
“Chinese firms feel limited impact from SVB’s failure; experts warn of global risks
By Ma Jingjing Published: Mar 12, 2023 07:19 PM

People look at signs posted outside of an entrance to Silicon Valley Bank in Santa Clara, California, on March 10, 2023. Photo: VCG
Some Chinese enterprises that have business ties with US-based Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) said that they have so far seen limited impact from the bank’s dramatic bankruptcy, but some analysts warned about risks posed by SVB’s collapse for global financial markets.
The bank’s fall laid bare the US government’s failed monetary and financial policies, and it may trigger a domino effect and have a negative impact on financial markets across the world, analysts noted.
The world saw the rapid collapse of the 16th-largest bank in the US on Friday, as it was shuttered and deposits seized by US regulators in a stunning 48-hour downward spiral. The lender announced in a surprise move on Wednesday that it needed to raise $2.25 billion to shore up its balance sheet, prompting depositors to withdraw their money amid anxiety over the bank’s health.
SPD Silicon Valley Bank (SSVB), a joint venture between Shanghai Pudong Development Bank Co and SVB, urgently clarified on Saturday that it’s an independent legal entity that is registered in China, with a standard corporate governance structure and an independent balance sheet.
As the first technology and innovation bank in China, SSVB is committed to serving Chinese technology entrepreneurs and maintains stable operations in line with China’s laws and regulations, read a statement on the company’s website.
SSVB previously said it’s focused on serving Chinese innovation-oriented firms and investors mainly in eight sectors, including healthcare, smart manufacturing, semiconductors and fintech.
As of the second quarter of 2022, the bank was serving more than 3,000 corporate clients, of which 31 were listed in China or overseas, domestic news site 21jingji.com reported.
Everest Medicines, a biopharmaceutical company in East China’s Zhejiang that is focused on the development, manufacturing and commercialization of innovative medicines and vaccines, said on Sunday that SVB’s collapse has had a limited impact on the company’s business, stressing that the company’s deposits at the bank are far lower than 1 percent of its total cash volume.
The firm said it’s expected to receive most of its deposits at SVB via the US Federal Deposit Insurance Corp (FDIC)’s insurance and other channels. It said that the amount of uninsured deposits is about $1 million, while it has no deposits at other US banks, according to a statement on the company’s WeChat account.
Firms cited China’s sound policy and financial environment and Chinese start-ups‘ strong growth momentum for the limited impact so far.
SVB’s fall is seen as the largest failure of a US bank since the financial crisis in 2008. The fallout from the collapse of the bank is starting to spread across the world, as the bank had developed relationships with tech start-ups and the venture capital community around the world over the past 40 years.
„SVB’s bankruptcy shows that the US‘ monetary policy is a total failure. The US Fed’s faster-than-expected tightening created turmoil in the global financial system and eventually harmed its own banking system,“ Li Yong, deputy chairman of the Expert Committee of the China Association of International Trade, told the Global Times on Sunday.
SVB saw a mass inflow of deposits in 2021 amid the ultra-loose monetary policy in the US. As it could not expand its loan business fast enough to generate revenue, the bank invested in longer-term mortgage securities with more than 10 years‘ duration, with a weighted average yield of 1.56 percent. However, the value of these securities tumbled along with the Fed’s rate hikes, leading to depositors‘ hurried withdrawal of their money.
Li warned that many US banks, especially small and medium-sized lenders, are in the same situation as SVB, which, if not appropriately managed, may set off systemic risks and cause a domino effect across the world.
Britain’s finance ministry and the Bank of England are working to minimize the disruption that could arise from a collapse of the UK arm of Silicon Valley Bank, Reuters reported. In addition, Israeli venture capital funds held emergency discussions on Saturday to formulate measures to help Israeli start-ups that cannot withdraw money from their bank accounts, according to media reports.
„Chinese authorities‘ strengthened regulation of the platform economy over recent years, especially policies that cracked down on monopolies and the disorderly expansion of capital, made Chinese start-ups much more immune to SVB’s collapse,“ Dong Shaopeng, a senior research fellow at the Chongyang Institute for Financial Studies at Renmin University of China, told the Global Times on Sunday.
„SVB’s crisis offers other countries a lesson that they shouldn’t rely too much on the US financial system, which has loopholes, and instead should maintain independent financial and technology policies,“ he said.
https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202303/1287139.shtml
Neben der Neugründung einer Superfinanzregulierungsbehörde, um Finanzkrisen aus dem Immobilien- und Hitechsektor, den verschuldeten Staatsbetrieben und Lokalregierungen und Regionalunternehmen sowie den schwarzen Banken als auch Kreditausfällen aus der Neuen Seidenstrasse zuvorzukommen, reguliert China jetzt auch noch weiter den Hitech- und Startup-Sektor mittels einer neuen Zentralen Technologiekommission, auch um ihn vor Risiken wie der Silicon Valley Bank zu bewahren und seinen Mix aus Industriepolitik und Unternehmertum in Zeiten von Decoupling und Hitechsanktionen und Handelskrieg in Richtung Selbstbehauptung und Unabhängigkeit zu fördern.
China ramps up sci-tech self-reliance drive with establishment of new central commission
By GT staff reporters Published: Mar 17, 2023 10:03 PM Updated: Mar 17, 2023 11:10 PM
Photo:VCG
China has announced to establish a central commission that will be in charge of reviewing major national strategies for scientific and technological development, one of the most powerful changes to the country’s innovation system in decades and which paves the way for the rollout of more policies to achieve core technological breakthroughs, experts said.
The commission’s establishment, part of a series of recently announced institutional reforms, is also seen by many as a response to a toughening crackdown from Western countries targeting China’s tech companies ranging from Huawei to TikTok, as the world’s second largest economy goes all out to break Western countries‘ scientific blockade in pursuit of „self-reliance“ in the tech sector.
The new commission, named the Central Commission for Science and Technology, will enhance the CPC Central Committee’s centralized and unified leadership over the work of science and technology, according to a plan released by the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on reforming Party and state institutions, the Xinhua News Agency reported on Thursday.
Its functions include pushing forward the building of a national innovation system and structural scientific and technological reform, studying and deliberating major strategies, plans and policies for the country’s sci-tech development, and coordinating efforts to resolve major issues of strategic, guiding and fundamental significance in the sci-tech sector.
It will also coordinate the deployment of strategic scientific and technological forces such as national laboratories, the plan said.
The responsibilities of the working body of the new commission are borne by the restructured Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST). A number of leadership groups related to science and technology have been scrapped.
Technological breakthroughs
According to experts, the establishment of the commission signals another lift to the strategic position of science and technology in China after the country designated science and technology primary productive forces, a theory put forward by Deng Xiaoping in 1988.
It not only reflects Chinese government’s strategic emphasis on science and technology, but will also greatly enhance decision-making and execution efficiency that will have a key role in pushing China’s key scientific and technological innovations in the days to come, experts said.
Ma Jihua, founder of Beijing DARUI Management Consulting Co and a veteran tech observer, told the Global Times on Friday that there were two major problems with MOST’s oversight of the science sector in the past. „First, they had too much routine work to attend to. Second, their administrative level was not high enough to directly coordinate with different ministries and enterprises,“ Ma said.
One consequence of this is that although China launched the national strategy of innovation driven development as early as in 2016, and a large amount of money has been poured into scientific research since then, there has not been enough of a shift from research into concrete industrial productivity, Tian Yun, a macroeconomic observer, told the Global Times on Friday.
China’s research and development expenditure rose 10.4 percent in 2022 to 3.1 trillion yuan ($448 billion), securing double-digit growth for seven years in a row, data released by the National Bureau of Statistics in January showed.
Experts also predicted that the new commission might soon make policy deployments to push research and application of core technologies such as chip production, new energy, new materials and artificial intelligence.
„The Central Commission for Science and Technology will likely plan to develop the Chinese chip industry by rolling out more specific measures, such as how to allocate policy resources and financial funds to boost the industry. They could also dispatch a team to implement relevant work,“ Tian said.
Ma also said that the commission will come up with more specific plans on new infrastructure development, detailing assessment indicators, development goals, people in charge and other matters.

Photo taken on Sep 22, 2022 shows an intelligent production base of the Great Wall Motors (GWM) in Yongchuan District of Chongqing, southwest China. Photo:Xinhua
Addressing external pressure
At the same time, setting up a top-level commission to oversee China’s science and technology sector is also a move seen by experts as China’s response and solution to a toughening global environment, with Chinese tech companies seeing an increasingly stringent crackdown and restrictions from certain Western countries.
The latest target of this crackdown is TikTok, which is facing another wave of suppression measures from the West.
Recently, the Biden administration has threatened to ban TikTok from the US unless the app’s Chinese owners agree to spin off their shares. The UK government has also banned the app from government phones as a result of so-called security concerns, according to a report by Sky News.
Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson Wang Wenbin said on Friday during a press conference that China has consistently insisted that data security issues should not become a tool for certain countries to generalize national security concepts, abuse national power, and unjustifiably suppress other countries‘ enterprises.
Prior to the TikTok incident, the US government had also rolled out many crackdown measures against China’s technological rise, such as issuing semiconductor-related export controls on China and enticing global chip giants to decouple from China’s supply chains.
Experts said that the new commission will gear the country up to better handle external crackdowns like those mentioned above, as the commission will give clearer, more timely and appropriate instructions on how to cope with external sanctions.
„When China faces major scientific and technological security issues, the Central Commission for Science and Technology can listen to reports and suggestions from various sides, formulate a response strategy as quickly as possible and urge relevant departments to implement them,“ Ma said, adding that such a mechanism will „reduce the cost of communication and enhance the speed of response. „
Chen Jia, a veteran economic observer, also told the Global Times on Friday that at a time when the Biden administration is imposing increasingly harsh sanctions on China’s science and technology sector, China must increase the strength of countermeasures in its top-level policy design as well as provide a comprehensive service system to help tech companies that are tapping overseas markets.
He also said that China could join hands with other developing countries to jointly oppose the rogue hegemonic behavior by certain countries to safeguard the interests of their tech companies.
https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202303/1287490.shtml
Zudem verringert China seit einiger Zeit kontinuierlich seine Eilange an US- Staatsschulden und hat diese nun auf von 1,3 Billionen US$ auf nun 850 Millairden US$ zurcükgefahren, zum einen um die immer grassierendern Risikien infolge der US- Verschuldung und Hochzinspolitik für sich selbst zu reduzieren, dann teils als Antwort auf das US- amerikanische Decoupling, diesmal mit umgekehrten Vorzeichen und auch als Beitrag zur Dedollarsierung und Internationalisierung des Yuan, auch mittles zunehmender Abwicklung des Handels in Yuan und Aufstockung des Yuanfinanzsytsmes über die New Development Bankk der BRICS und Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) sowie anderer Fianzinstitutionen. Jedenfalls ist man stolz, seinen Anteil an den US- Staatsschulden unter die 1 Billionenmarke gedrückt zu haben, wenngleich man auch nicht mit der „nuklearen Option“ eines sofortigen umfassenden Verkauf amerikanischer Staatsschuldenpapier droht. Der protartcted war vollzieht sich momentan noch garduell, aber stetig eskalierend. Wenngleich China sich auch schon vor der SVBkrise mit US- Finanzministerin Yellen getroffen hatte, da es die kommenden Instabilitäten auf den Finanzmärkten scheinbar kommen sah und dem zuvorkommen wollte. Unilateral tat dies die KP China ja dann mittels der Schaffung der neuen Finanzregulierungsbehörde nach dem Nationalen Volkskongress. Zudem verweist man noch stolz auf einen Überschuss an ausländischen Wärhungsreserven von 3.13 Billionen US$.
„Washington has itself to blame for China’s cut in US Treasury holdings: expert
By Ma Jingjing Published: Mar 16, 2023 03:38 PM

A teller counts U.S. dollar bills at a bank in Qionghai, south China’s Hainan Province.Photo:Xinhua
China reduced its holdings of US Treasury debt for the sixth straight month in January, which analysts said was mainly due to the US Federal Reserve’s rate hikes and China’s long-term security-driven diversification of its foreign exchange reserves.
The US Department of the Treasury released data on Wednesday (local time) showing that China’s holdings of US Treasury debt dropped to $859.4 billion in January, declining for the sixth straight month and falling below $1 trillion, where it has been for every month since last April.
China’s holding of US government debt is at its lowest since May 2010, when it held $843.7 billion.
However, China remains the second-largest non-US holder of US debt after Japan, which held $1.104 trillion as of the end of January.
Slashing investments in US Treasuries, which are an important component of China’s $3 trillion-plus in foreign reserves, shows the flexibility of Chinese financial institutions‘ asset allocation and the diversification of investment portfolios, amid higher dollar interest rates and a volatile international environment, analysts noted.
„The value of US Treasuries started to fall when the US Federal Reserve started to hike interest rates in March 2022, while asset values in other developed economies such as the EU and Japan were relatively higher due to lower interest rates.“ Zhao Qingming, a Beijing-based veteran financial expert, told the Global Times on Thursday.
„As a method to optimize investment, it’s natural for Chinese institutions to cut holdings of US government debt,“ Zhao said.
After seven aggressive interest rate hikes to tame inflation in 2022, the Fed raised the target for the federal funds rate by 0.25 percentage points in February. Generally, investors tend to sell off US Treasuries when interest rates increase, given their demand for higher bond returns.
China’s holdings of US Treasuries fell below $1 trillion for the first time in 12 years last April.
The second-largest creditor’s fire sale signals waning confidence, as the US faces economic woes such as its debt ceiling debacle and turmoil in its banking sector, Gao Lingyun, an expert at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences in Beijing, told the Global Times on Thursday.
The US has only itself to blame, Gao said. „It’s time for the Biden administration to stabilize the US economy and its financial policies to create more certainty for global investors,“ he told the Global Times on Thursday.
Foreign countries may now be less motivated to sell off US Treasuries, as the Fed is expected to slow down interest rate hikes in the coming months, Zhao forecast.
However, it could be a long-term trend for China to diversify its foreign exchange reserves faster into other currencies or assets, as the US‘ weaponization of the dollar poses greater risks for holders of US Treasuries, according to Chinese experts.
The US has used its financial services as a weapon against Russia amid the Russia-Ukraine conflict to a scale and depth unseen before. Taking it as a lesson, countries around the world have recognized the importance of diversifying their dollar-denominated assets.
For example, Iraq’s central bank is reportedly planning to settle trade from China in yuan for the first time to improve its access to foreign currency, Reuters reported.
China has been promoting the use of the yuan in bilateral trade and investment over recent years. It has become the world’s fifth-largest payment currency, third-largest currency in trade settlement and fifth-largest reserve currency, official data showed.
China’s foreign exchange reserves stood at more than $3.13 trillion at the end of February, down $51.3 billion, or 1.61 percent, from the end of January, according to latest data released by the State Administration of Foreign Exchange.